Psoriasis
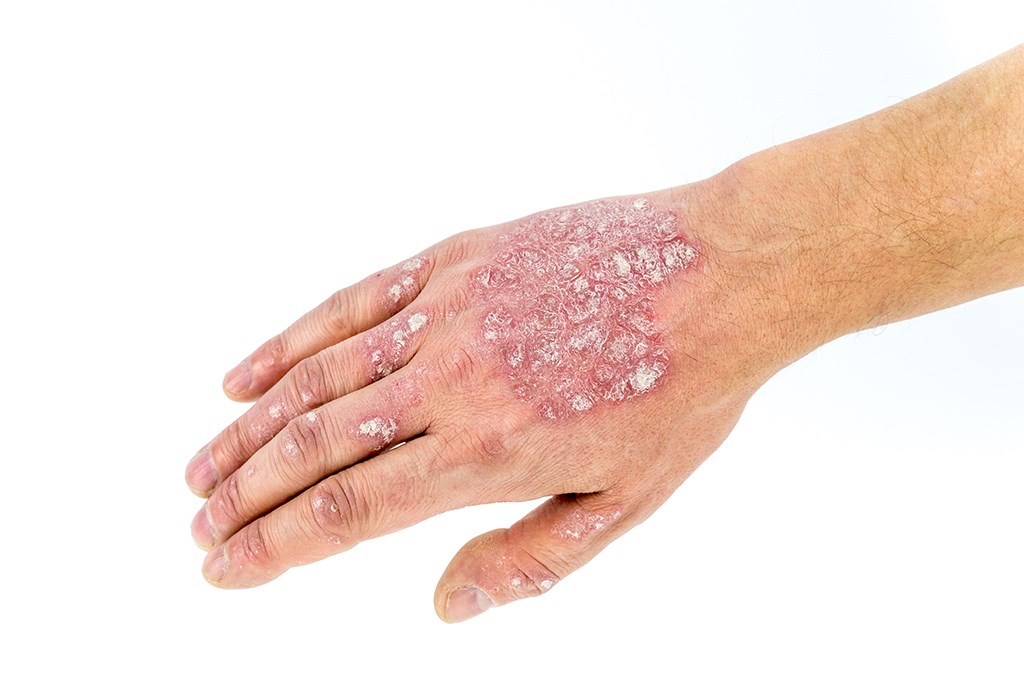
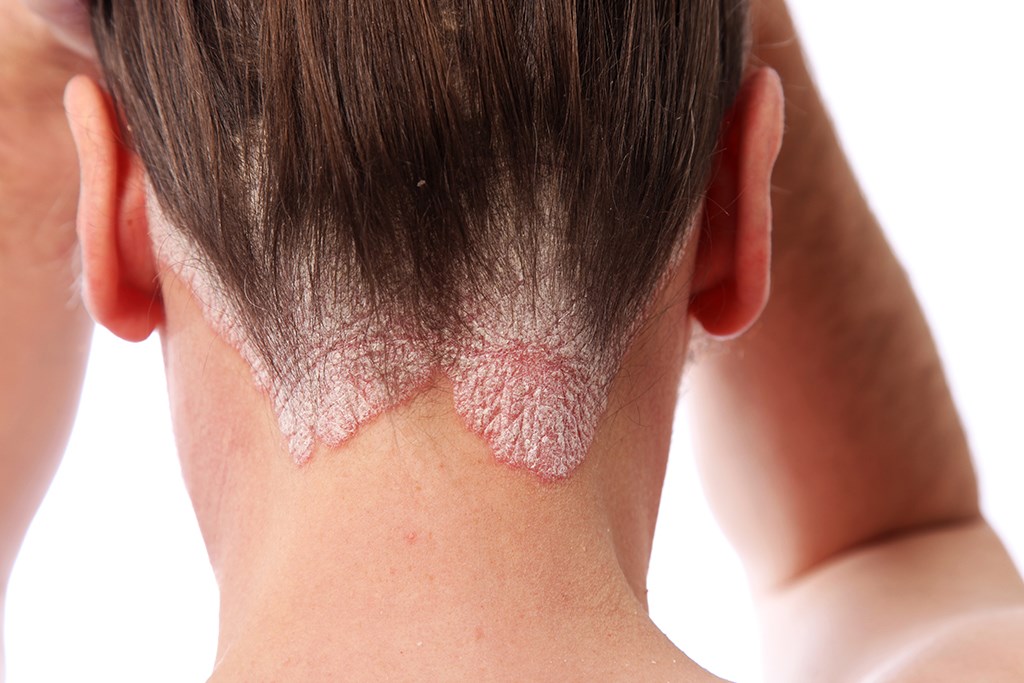
Psoriasis is a chronic disease when a person’s immune system causes skin cells to grow too rapidly. The body does not shed the excess skin cells, leading to patches on the skin. Psoriasis is not contagious. Research suggest that a combination of genes and exposure to specific external factors, known as triggers cause a person to develop psoriasis. Some triggers include stress, infections, such as streptococcal, physical trauma (rubbing and scratching), and certain medications. Psoriasis can occur at any age, but most people develop it between the ages of 15 and 30. Early onset of the disease usually predicts a more severe and long lasting disease.
Psoriasis can occur on many areas of the body, including the scalp, fingernails, palms of hands, soles of feet, knees, elbows, body folds, perianal and genital area. Psoriasis can also occur on the trunk in some people.
People with psoriasis have an increased risk for developing other chronic health problems, or comorbidities, including psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, depression and metabolic syndrome.
Treatment
There are a variety of treatment options for psoriasis ranging from topical medications that are applied to the skin to biologic agents that are administered by injection.