Acne
Acne is the most common skin disorder in the United States. Acne more commonly occurs from puberty – 17 years of age for females, and from 14 -19 in males. Usually the disease will stop before the age of 25. However, some people may continue to have acne throughout their adult years.
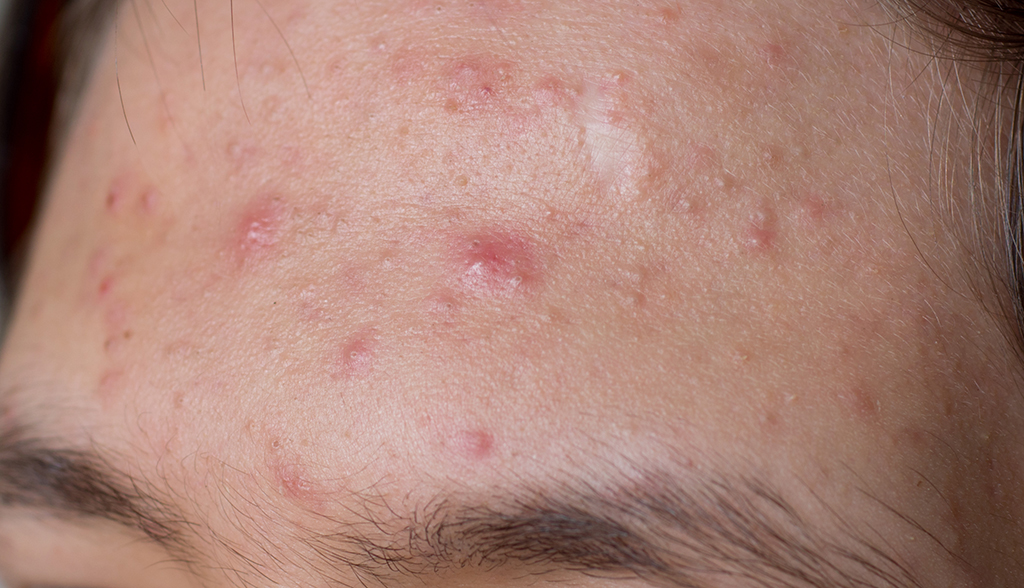
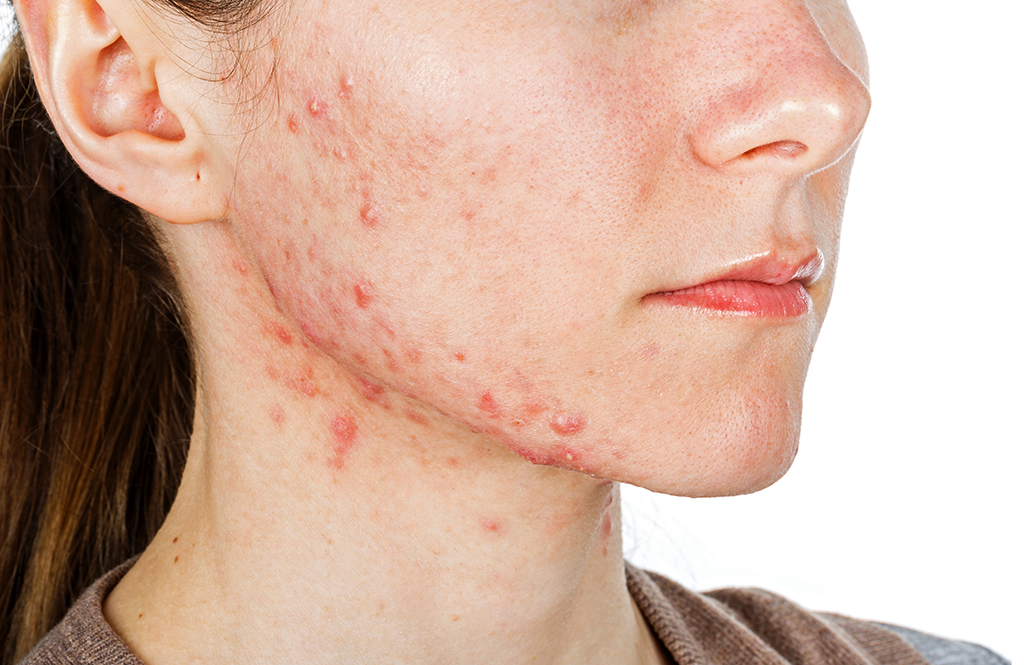
Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory disease of the pilosebaceous follicles. It most commonly affects the face, neck, chest, shoulders and upper back, which have a high concentration of sebaceous follicles. Acne occurs when keratinous material (dead skin cells) in the follicle does not shed normally. This material becomes dense and blocks the secretion of sebum (oil). These plugs are a type of acne lesion known as comedones (black and white heads). As the follicle opening becomes more plugged up, the lower portion of the follicle becomes more enlarged due to the trapped sebum. This leads to inflammation in the pilosebaceous unit. The distended follicle wall eventually will break, and the contents will enter into the dermis of the skin. This provokes an inflammatory response in the skin and leads to the papules, pustules, nodules and cysts of acne. This all occurs due to a complex interaction between bacteria (propionibacterium acnes) and androgens (hormones). Androgens stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce larger amounts of sebum.
There are contributory factors that can aggravate existing acne such as certain medications, occlusion, and pressure (for example: leaning face on hands, chin straps, hats). Also, scrubbing of the face during washing will increase irritation and often worsen the acne due to friction. Though people commonly believe that fatty foods and chocolate make acne worse, no evidence exists that dietary choices have an effect on the severity of acne.
Treatment
Treatment varies depending on the type of acne. Options include: topical medications that are applied directly to the skin surface, oral antibiotics, oral hormonal therapy or oral isotretinoin therapy. Topical medications may take 8 weeks or more before improvement starts to occur. The topical medications are to be applied to the entire affected area, not just the lesions. Oral antibiotics are taken by mouth in pill form, and it generally takes about 6 to 8 weeks to begin to see improvement. Isotretinoin is a medication taken by mouth for usually about 6 months. This medication is used in people with severe cystic acne, or in people with acne not responding well to other treatments. There are potential serious side effects while taking isotretinoin, so monthly follow-up while on this medication is mandatory.
Levulan Photodynamic Therapy with Blue Light
Acne skin care treatment using Levulan Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) from Dusa Pharmaceuticals is the most recent advance in acne treatment. PDT is a 2-part process that involves the application of Levulan topical solution (5-amniolevulinic acid), a photosensitizing agent, which is then activated with Blue Light. This results in significant improvement in moderate to severe cystic acne, and can also be used to treat Actinic Keratoses (AK), sun damaged and oily skin.
PDT involves three mechanisms of action against acne. The Levulan treatment inactivates the bacteria that trigger acne and exfoliates the skin to unclog pores. The most exciting mechanism is that Levulan treatment shuts down the sebaceous glands in the skin. This is exciting because sebaceous glands are the root cause in the formation of acne, so the treatment has a long-lasting effect even on severe acne.
PDT can even work in patients who have not responded to Accutane. Accutane also targets the sebaceous glands but has fairly toxic side effects. PDT is a very safe alternative to Accutane treatment.
The Blue Light Treatment is not a laser. It emits safe, cool, visible, blue light to provide an effective solution for improvement of acne.
Typically, a series of three to four treatments is performed 3-4 weeks apart. At each treatment, the area will be scrubbed with acetone or a microdermabrasion will be done. This preps the skin and allows for better penetration of the Levulan. The Levulan is then applied to the treatment area and left on the skin for 30 minutes to three hours depending on the area to be treated. After the desired incubation time, the Levulan is removed with alcohol, and the treatment is performed with the Blue Light. Afterward, the area will be washed with soap and water to remove residual Levulan, and a sunblock is applied.
Chemical Peels
Patients who have seen the best results in reducing their acne and preventing future breakouts have had a series of 6 peels, spaced 3-6 weeks apart, and have combined the treatment with at-home skin care products.